Navigating the Digital Transformation: Marketing Strategies in the UK Luxury Fashion Industry

Marcus Binnie
Marcus Binnie is a 4th year marketing student with a passion for the luxury fashion industry. He focuses on digital transformation and innovative marketing strategies. Read more of his insights on Navigating the Digital Transformation: Marketing Strategies in the UK Luxury Fashion Industry.
Introduction
The luxury fashion industry, known for its exclusivity, high-quality craftsmanship, and premium pricing, is one of the most dynamic and influential sectors in the global market (Choi & Liu, 2019). Renowned brands such as Burberry, Alexander McQueen, and Stella McCartney not only set trends but also symbolise status and sophistication (Ma, 2022). In an era where digital presence and consumer engagement are paramount, luxury fashion brands must innovate their marketing strategies to maintain their elite status and captivate a discerning audience (Wang, 2021).
Blog Content
This blog focuses on exploring the intricate and multifaceted marketing strategies employed by luxury fashion brands. While traditional marketing techniques have their place, the digital revolution has transformed how these brands interact with their audience (Liu, 2023). From leveraging social media influencers to creating immersive online experiences, luxury fashion brands are continually adapting to the evolving digital landscape (Zhang, 2023). This blog will delve into the current state of the luxury fashion market, highlight key marketing trends and issues, and provide detailed case studies of how leading brands are navigating this complex environment (Matić & Bajs, 2022).
By analysing these elements, we aim to understand not only the effectiveness of various marketing strategies but also their impact on brand perception and consumer behaviour (He, Jiang, & Wang, 2022). The insights gained will offer valuable recommendations for future marketing endeavours within the luxury fashion industry, emphasising the importance of a well-rounded and adaptive approach to digital marketing (Zhang, 2023).
The Rise and Rise of Influencer Marketing
According to The State of Influencer Marketing Report, the Fashion & Beauty sector leads the way in influencer marketing, with 21.6% of brands incorporating it as a core strategy. Among the most frequently mentioned fashion brands by influencers are Zara, Shein, H&M, NA-KD, Pretty Little Thing, and ASOS. Following closely, the Gaming sector sees 11.9% of brands significantly increasing their investment in influencer marketing efforts (20 surprising influencer marketing statistics 2024).
This highlights the increasing reliance on influencer marketing within the fashion industry, demonstrating its effectiveness in reaching broader and younger audiences.
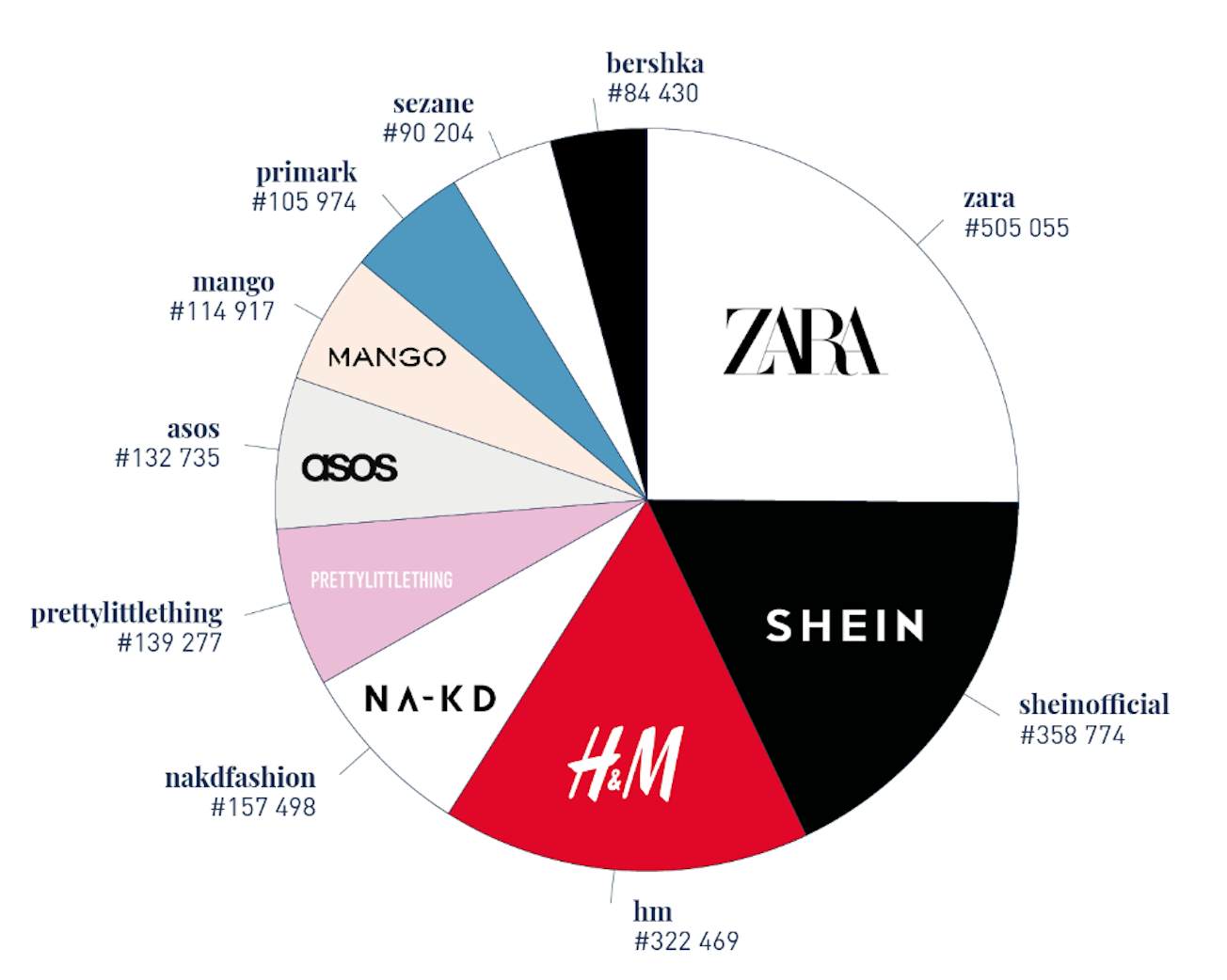
Top 10 most mentioned fashion brands by influencers.
Immersive Tech Week: Virtual Fashion and Virtual Bodies
Beatril Check, a speaker at the event featured in the video (Immersive Tech Week 2022 | Virtual Fashion & Virtual Bodies, 2023), works at the intersection of fashion and technology, focusing on sustainability and digital transformation. She founded Unfolding Strategies, a consultancy that provides design and virtual training, produces a podcast on digital fashion, and conducts research and strategy for fashion brands. Additionally, she joined the NFT marketplace, The Dematerialized.
Unfolding Strategies is a consultancy and education lab dedicated to promoting digital, diverse, and sustainable fashion. The company offers services like design and virtual training, a podcast discussing various aspects of digital fashion, and strategic research partnerships with fashion brands. Their work aims to future-proof and reimagine the fashion industry by integrating digital and sustainable practices.
Digital fashion is defined as fashion created using digital tools, intended for either virtual or physical use. Examples include virtual-only fashion utilized in gaming, social media, and collectibles, as well as digital garments available through filters. The concept of "phygital" fashion merges physical and digital elements, creating a blend that expands traditional fashion boundaries.
The promises and paradoxes of digital fashion are multifaceted. In terms of sustainability, digital fashion has the potential to support sustainable development goals, but its environmental impact requires further investigation. Accessibility is enhanced as digital fashion allows broader participation without geographic constraints, although it also contributes to the digital divide. Creativity in digital fashion is limitless, offering unprecedented design possibilities, but often results in a singular aesthetic influenced by sci-fi and cyber themes.
Digital fashion applications include ownership and collection, where digital garments can be owned and collected; co-design, allowing consumer participation in the design process; and resale and wear, with digital fashion worn virtually in games or on social media, and resold in virtual markets. Various platforms like Decentraland, Zepeto, Meta, Roblox, and IMVU provide different experiences and body representations, showing varying levels of customization, diversity, and aesthetic quality.
The Web 3.0 Body Atlas project explores diversity and identity representation in virtual avatars. Participants are encouraged to contribute by scanning QR codes and submitting their avatars, aiming to understand better and support diverse body types and identities in virtual spaces.
Implications for Marketing
New Marketing Strategies: The rise of platforms like The Dematerialized and other virtual marketplaces means fashion brands need to develop strategies for selling digital-only products. Marketing strategies can leverage NFTs to create unique digital assets that offer consumers exclusive ownership and experiences.
Engagement and Experience: Brands can create immersive experiences in virtual worlds (e.g., Decentraland, Roblox) that engage consumers in new ways, building brand loyalty and community. Using AR filters to allow consumers to try on digital garments can enhance the shopping experience and drive engagement.
Content and Community: Content creation, such as podcasts on digital fashion, can educate and engage audiences, positioning brands as thought leaders in the digital fashion space. Collaborating with digital influencers and creators who are prominent in virtual spaces can amplify brand reach and authenticity.
Data and Insights: Digital fashion provides rich data on consumer preferences and behaviors, allowing for more targeted and effective marketing campaigns. The co-design process offers immediate feedback, enabling brands to refine their offerings based on consumer input.
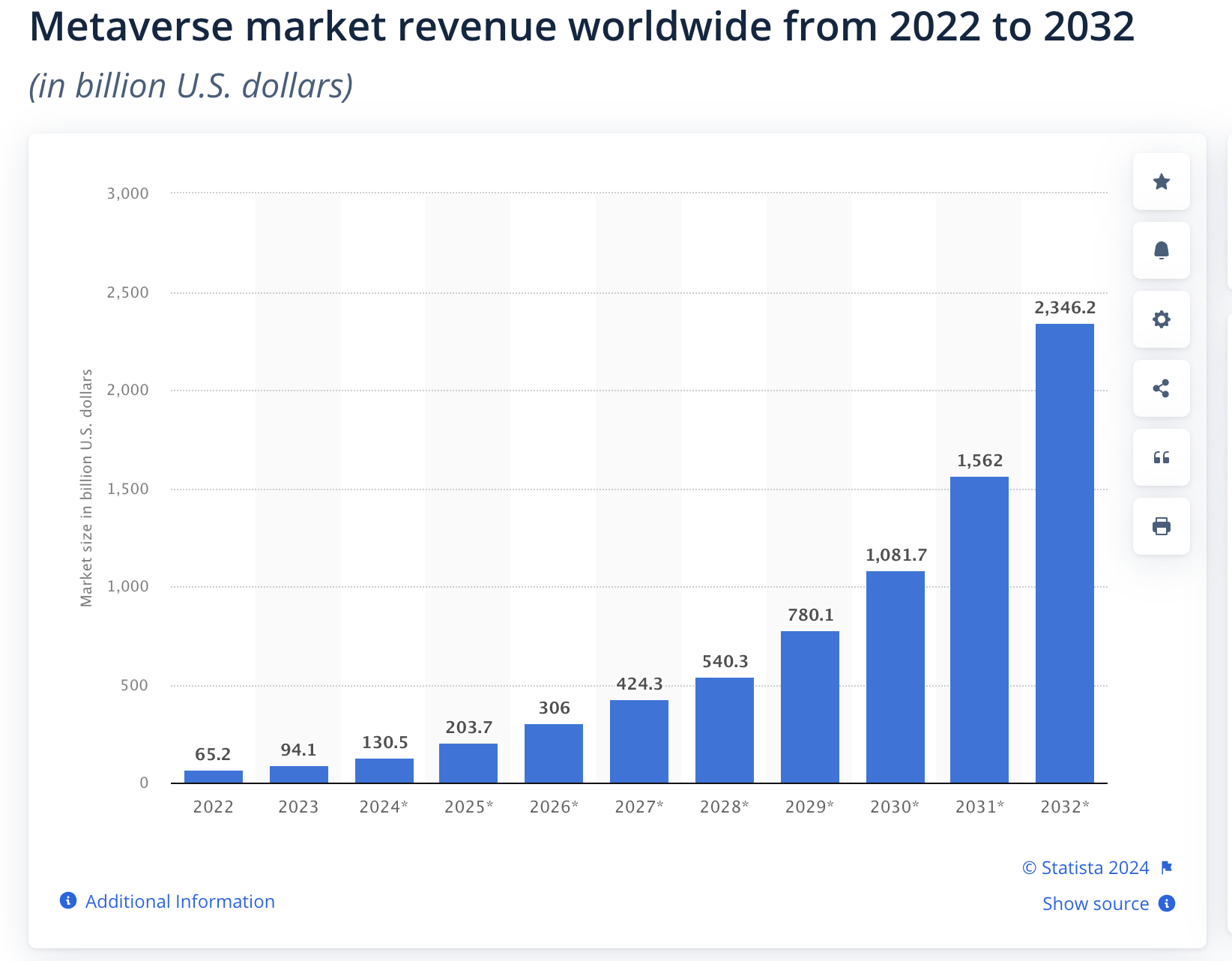
(Alsop, 2024)
Future Outlook
As technology advances, the integration of AI, machine learning, and blockchain will further transform digital fashion, creating new opportunities and challenges for both fashion and marketing. Brands will need to navigate ethical considerations around digital fashion, including environmental impacts, digital inclusivity, and data privacy.
Overall, the fusion of fashion and technology spearheaded by thought leaders like Beatril Check is driving a paradigm shift in how fashion is created, marketed, and consumed, emphasising sustainability, inclusivity, and innovation.
One brand that is embracing the metaverse is Louis Vuitton. In this video, I cover all the main points and future outlook for Louis Vuitton to revolutionise the fashion industry.
Insights from SEMrush Data and Forbes on Luxury Fashion's Metaverse Transformation - An Overview of Key Players in Luxury Fashion
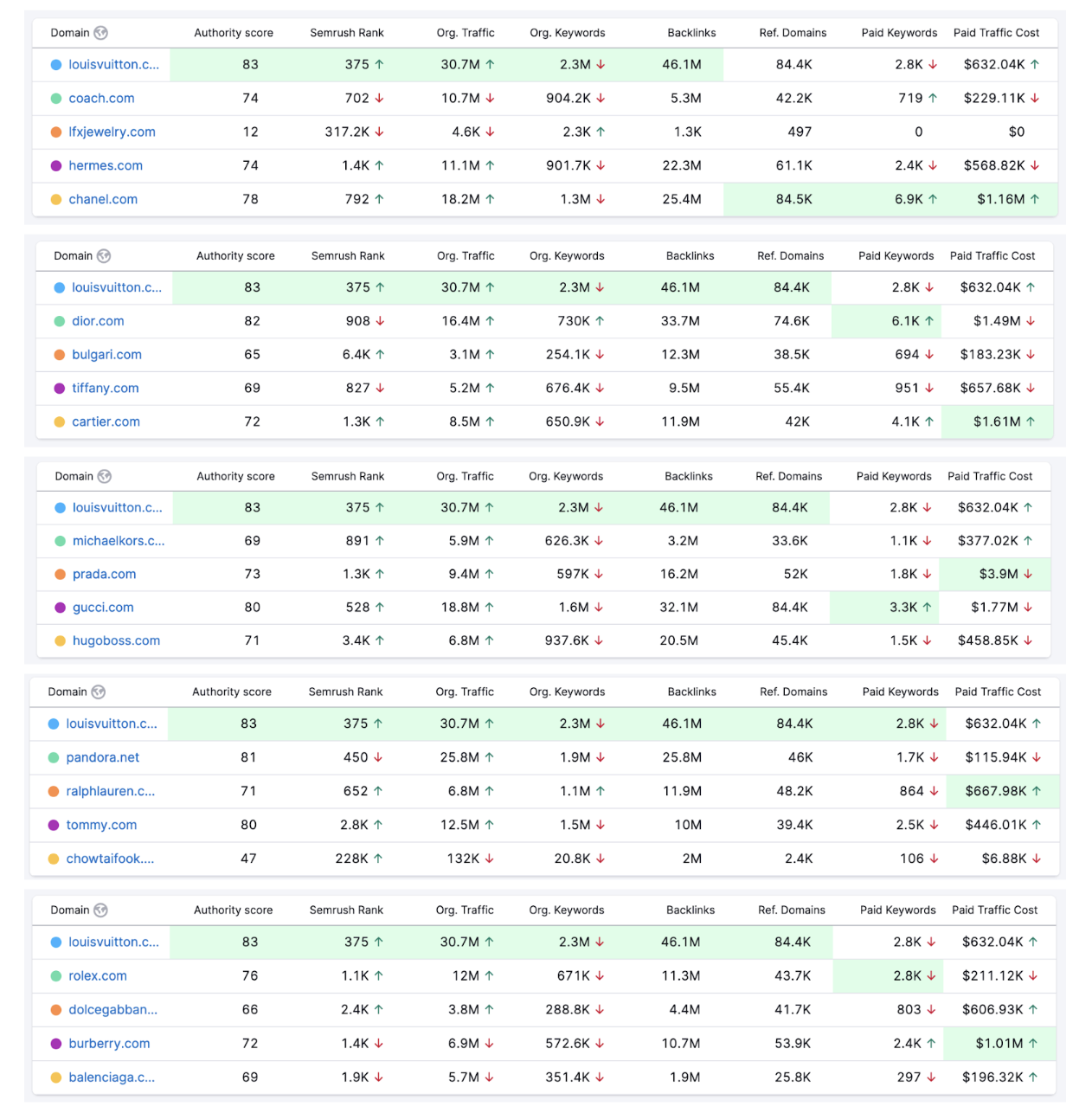 Comparative analysis of luxury brands using SEMRush data.
Comparative analysis of luxury brands using SEMRush data.
Immersive Experiences and Digital Presence: Luxury fashion brands like Louis Vuitton, Gucci, and Balenciaga are pioneers in adopting metaverse technologies, creating immersive experiences that engage consumers in virtual worlds. The SEMrush data showing high organic traffic for these brands indicates their successful digital strategies. For example, Louis Vuitton's robust organic traffic of 30.7M highlights its strong online presence and effectiveness in attracting visitors through organic search.
Strategic Use of Digital Platforms: These brands are leveraging platforms like Decentraland and Roblox to create engaging virtual experiences, as seen with Gucci's virtual garden in Roblox. This strategy is reflected in the significant number of organic keywords and backlinks, such as Gucci's 1.6M organic keywords and 32.1M backlinks, demonstrating their commitment to SEO and content marketing to enhance visibility and engagement in the digital space.
NFTs and Exclusive Digital Assets: The integration of NFTs into their marketing strategies allows brands to offer exclusive digital assets, enhancing consumer engagement and creating new revenue streams. The SEMrush data shows a substantial investment in paid keywords and traffic costs, like Chanel's $1.16M in paid traffic cost, indicating a strong emphasis on digital advertising to promote these unique digital products.
Building Digital Communities: Luxury brands are also focusing on building communities within virtual worlds, fostering brand loyalty and enhancing the consumer experience. The high number of referring domains for brands like Louis Vuitton (84.4K) and Chanel (84.5K) suggests a wide-reaching influence and strong network of online mentions and collaborations, crucial for community building.
Continuous Evolution and Innovation: The article emphasizes the need for luxury brands to continuously innovate and adapt to the evolving digital landscape. The SEMrush data indicates that top luxury brands are already investing heavily in digital transformation, as evidenced by their high authority scores and comprehensive digital marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Integrating insights from the Forbes article with SEMrush statistics reveals that luxury fashion brands are at the forefront of digital innovation, leveraging immersive commerce, NFTs, and strategic digital marketing to maintain their competitive edge. These efforts are reflected in their strong online presence, high organic traffic, and significant investment in both organic and paid search strategies. This comprehensive approach ensures that luxury brands not only stay relevant in the digital age but also lead the way in shaping the future of fashion in the metaverse era (Boyd, 2023).

Louis Vuitton is an online market leader, as indicated by SEMRush.

Current Situation
The luxury fashion market in the UK is currently navigating a complex landscape marked by significant shifts in consumer behaviour, technological advancements, and economic uncertainties. The industry, long associated with timeless elegance and exclusivity, is now compelled to adapt to the rapidly changing digital era (Rahman, 2023).
Market Overview
In recent years, the UK luxury fashion market has witnessed substantial growth, driven by rising disposable incomes and an increasing appetite for high-end products among consumers (Kim & Lee, 2011). Brands such as Burberry and Mulberry have solidified their positions as iconic British luxury labels, contributing to the global reputation of UK fashion (Tsai, 2005). However, the market faces challenges from both internal and external factors, including Brexit-related economic uncertainties and the aftershocks of the COVID-19 pandemic, which have affected consumer spending patterns and supply chain operations (Cassidy, 2017).
Digital Transformation
One of the most significant trends shaping the current luxury fashion market is digital transformation. As highlighted by Zhu (2023), the Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards digital sales, compelling brands like Burberry to adapt their strategies (Zhu, 2023). Additionally, Kim and Ma (2019) demonstrate how digital transformation can enhance brand value and consumer engagement through innovative digital strategies (Kim & Ma, 2019). Brands like Louis Vuitton exemplify the blend of tradition and modernity, effectively balancing their historical values with contemporary digital marketing strategies. For start-up luxury brands, digitalisation strategies are crucial to overcoming challenges of smallness and newness, as highlighted by Rosenbaum et al. (2022). The study on Vidda Royalle demonstrates how leveraging unique digital strategies can enable start-up luxury brands to compete effectively with established incumbents (Rosenbaum et al., 2022). With the rise of e-commerce and social media, luxury brands are investing heavily in their online presence (Kohrs, 2020). Digital channels have become crucial for engaging with a broader audience and providing a personalised shopping experience. The use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in online platforms allows customers to experience products in innovative ways, enhancing the shopping experience and driving sales (Hilken et al., 2021; Riar et al., 2022).
Leveraging Digital Platforms for Engagement
In the digital age, fashion brands have unprecedented opportunities to connect with their customers. As noted by Rosenbaum et al. (2022), start-up luxury brands can enhance their online customer journey through strategic digital marketing efforts, creating a competitive edge in the market (Rosenbaum et al., 2022). Polat (2021) outlines how luxury brands are integrating digital strategies into their marketing plans, creating omnichannel experiences that engage consumers across various platforms (Polat, 2021). Platforms like social media, brand websites, and mobile apps are now central hubs for interaction. These digital spaces enable brands to share content, gather feedback, and engage in meaningful two-way conversations, thereby fostering a deeper emotional connection with consumers (Grassi, 2020; Wrigley & Straker, 2019).
Integrating Innovative Pricing Models in Digital Transformation
Research by Wood, Watson, and Teller highlights that many online fashion retailers still rely on traditional pricing methods like cost-plus and competitor alignment, despite the availability of advanced analytics and real-time data. To remain competitive, luxury brands should integrate innovative pricing models that consider customer value and dynamic market conditions. This approach can enhance profitability and customer satisfaction, aligning with broader digital marketing strategies (Wood et al., 2021).
Consumer Behaviour
Today's luxury consumers are more discerning and informed than ever before. They seek authenticity, sustainability, and personalised experiences. Younger generations, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, are influencing market trends with their emphasis on ethical consumption and social responsibility. This shift has prompted luxury brands to adopt more transparent and sustainable practices, from sourcing materials to production processes (Henninger et al., 2017).
Key Marketing Issues
Several key marketing issues have emerged in the luxury fashion sector. Romo et al. (2017) emphasise the importance of storytelling and social networking in digital and mobile marketing strategies, which are crucial for engaging with today’s tech-savvy consumers (Romo et al., 2017). Firstly, maintaining brand exclusivity while expanding digital reach is a delicate balance. Brands must innovate without diluting their luxury image. Secondly, the integration of technology into marketing strategies requires significant investment and expertise, presenting a barrier for some brands (Savelli, 2011). Lastly, the increasing importance of sustainability poses both a challenge and an opportunity. Brands need to demonstrate genuine commitment to sustainable practices to gain and retain consumer trust (Peng et al., 2017).
Conclusion
The current situation in the UK luxury fashion market is characterised by rapid digitalisation, evolving consumer expectations, and economic challenges. As brands navigate these complexities, the ability to effectively leverage digital marketing strategies, maintain exclusivity, and commit to sustainability will determine their success in this competitive landscape.

Key Marketing Issues
The UK luxury fashion industry is grappling with several significant marketing challenges that require strategic navigation to sustain growth and maintain market relevance. These challenges include economic uncertainties, digital transformation, sustainability demands, evolving consumer behaviour, and supply chain disruptions.
Economic Uncertainty
Economic volatility remains a critical concern for the luxury fashion sector. Factors such as geopolitical tensions, inflation, and potential recessions impact consumer spending power. In Western markets, economic instability has led to a cautious approach to spending, particularly on non-essential luxury items. Luxury brands must therefore emphasise the enduring value and investment potential of their products to appeal to consumers who are more selective with their expenditures (Brun et al., 2008; Olatubosun et al., 2021).
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is reshaping the luxury fashion industry, driving brands to invest heavily in their online presence and digital marketing strategies. The rise of e-commerce and social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok has created new avenues for consumer engagement. Brands are utilising technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to provide immersive online shopping experiences. However, this shift also requires maintaining the exclusivity and premium image associated with luxury brands, which can be challenging in a highly accessible digital environment (Duma et al., 2020; Kim & Ko, 2010).
Sustainability Demands
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern but a central issue for the luxury fashion industry. Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency in sourcing, ethical production practices, and efforts to reduce environmental impact. This includes addressing textile waste, carbon emissions, and sustainable supply chain practices. Brands that fail to demonstrate genuine commitment to sustainability risk losing consumer trust and market share. Successful brands are those that integrate sustainable practices into their core business strategies and communicate these efforts effectively to their audience (Franco et al., 2019; Karaosman et al., 2020).
Evolving Consumer Behaviour
Consumer preferences in the luxury fashion market are evolving, driven by younger generations who prioritise authenticity, social responsibility, and personalised experiences. The trend towards "quiet luxury," which emphasises understated elegance and craftsmanship over ostentation, reflects a broader shift towards more sustainable and conscious consumption. Brands must adapt their marketing strategies to align with these values, leveraging digital channels and influencer partnerships to engage with this discerning demographic (Han et al., 2017; Jung & Jin, 2016).
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical factors and the COVID-19 pandemic, continue to challenge the luxury fashion industry. These disruptions affect the availability of raw materials and finished goods, leading to delays and increased costs. Brands are responding by diversifying their supply chains, investing in local production capabilities, and using data analytics to optimise inventory management. Addressing these challenges requires a flexible and resilient approach to supply chain management (Brito et al., 2008; Macchion et al., 2015).
Conclusion
The luxury fashion industry in the UK faces a multifaceted landscape of challenges that require innovative and strategic responses. By addressing economic uncertainties, embracing digital transformation, committing to sustainability, understanding evolving consumer behaviours, and managing supply chain disruptions, luxury brands can navigate these issues effectively. This strategic approach will help maintain their market position and appeal to an increasingly discerning and socially conscious consumer base.
Case Studies: Marketing Strategies in Luxury Fashion
1. Gucci’s Digital Innovation and Hip Hop Influence
Gucci has leveraged digital innovation to maintain its market dominance effectively. The brand’s early adoption of e-commerce and continuous investment in online infrastructure have catered to the digital preferences of the millennial demographic, which constitutes a significant portion of its customer base. Gucci’s redesigned e-commerce platform includes features such as find-in-store options, comprehensive product information, and enhanced customer service. Additionally, Gucci’s integration with hip hop culture has boosted its popularity among younger consumers. The brand’s alignment with influencers and musicians has solidified its presence in popular culture, leading to record sales driven by consumers under 35 (Gucci Digital Marketing, Advertising & Strategy Case Study: G & Co.., 2024).

2. Louis Vuitton’s Blend of Tradition and Modernity
Louis Vuitton exemplifies the balance between maintaining traditional luxury values and embracing modern marketing strategies. The brand's steadfast commitment to premium pricing and high-quality craftsmanship has preserved its exclusivity. Simultaneously, Louis Vuitton’s digital advertising strategies, such as the Make A Promise campaign with UNICEF, demonstrate its ability to engage with contemporary issues and digital audiences. The brand’s innovative use of social media and influencer collaborations, including high-profile events and campaigns, has reinforced its market position and appeal to younger generations (Louis Vuitton, a Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study, 2023; This is how Louis Vuitton mastered the art of timeless luxury with these marketing strategies 2024).
3. Burberry’s Personalisation and Experiential Marketing
Burberry employs advanced personalisation techniques and experiential marketing to enhance customer engagement. By using machine learning algorithms, Burberry tailors its email communications to individual customers, enhancing the sense of exclusivity. The brand also collaborates with social media influencers and celebrities to design unique capsule collections that resonate with younger audiences. Burberry’s fashion shows and flagship store experiences incorporate cutting-edge technology, such as augmented reality, to create immersive brand interactions. These strategies have helped Burberry stay relevant and appealing in a fast-paced retail environment (Mastering luxury: Burberry Marketing Strategies & Marketing Mix 2023).

4. Localised Marketing Strategies in China
Luxury fashion brands have adopted localised marketing strategies to cater to the Chinese market. Brands initially used standardised global strategies but have increasingly tailored their approaches to fit regional preferences. This includes adapting product designs and introducing Chinese brand names to better resonate with local consumers. Such localisation efforts have proven essential for successful market penetration and growth in China, the world’s second-largest luxury market. This strategy highlights the importance of cultural sensitivity and regional adaptation in global marketing (Bai et al., 2021).

Conclusion
These case studies illustrate how leading luxury fashion brands successfully navigate the complexities of the modern market. By blending tradition with innovation, embracing digital transformation, and localising strategies for key markets, these brands maintain their prestigious status while appealing to new consumer segments. Understanding these strategies offers valuable insights for anyone looking to thrive in the competitive luxury fashion industry.
Recommendations for the UK Luxury Fashion Industry
The UK luxury fashion industry is poised for continued growth but must navigate several complex challenges. Based on the latest analysis, here are some key recommendations for luxury fashion brands to thrive in this dynamic market.

Recommendations
Suggested Strategies for Future Marketing
- Invest in Digital Innovation and Personalisation
- Kim and Ma (2019) highlight that digital transformation not only enhances customer engagement but also reinforces brand identity and value (Kim & Ma, 2019).
- Luxury brands should continue to enhance their digital presence by investing in technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create immersive shopping experiences. Personalisation should be a key focus, with tailored marketing and product recommendations based on customer data.
- In 2024, the UK luxury fashion market generated £5.7 billion in revenue, with an expected annual growth rate of 4.07% from 2024 to 2028. This underscores the necessity for ongoing digital innovation to harness this growing market. Comparatively, the US leads with a revenue of £21.5 billion in 2024. The revenue per capita in the UK is £84.80, highlighting substantial market potential. British designers like Burberry and Alexander McQueen are at the forefront of innovation and craftsmanship, driving the market’s success (Statista, 2024).
- For start-up luxury brands, digitalisation strategies can be particularly effective. Rosenbaum et al. (2022) suggest that leveraging unique digital strategies and managing the 'internet dilemma' of marketing high-value brands online can enhance competitive advantage and market presence (Rosenbaum et al., 2022).
- Example: Gucci’s successful digital transformation highlights the importance of a robust online platform and innovative digital engagement strategies (Gucci Digital Marketing, Advertising & Strategy Case Study: G & Co., 2024).
- Strengthen Sustainability Practices
- Implementing sustainable practices is crucial for luxury brands to meet consumer demands for ethical and environmentally friendly products. This includes sourcing eco-friendly materials, ensuring ethical production processes, and being transparent about sustainability efforts.
- Example: Brands that integrate sustainability into their core business strategies not only enhance their reputation but also build stronger consumer loyalty (Luxury fashion market size, share, industry analysis 2024-32, 2023; Nichols, 2023).
- Adapt to Changing Consumer Preferences
- British designers such as Burberry and Alexander McQueen are leading the way in innovation and craftsmanship (Statista, 2024). Burberry is known for integrating technology into their fashion, such as the use of RFID tags in their products and their pioneering efforts in digital marketing, including live-streaming fashion shows and partnering with platforms like Twitch to reach broader audiences (Hall, 2020; O', 2024). Alexander McQueen is renowned for his avant-garde designs and meticulous tailoring, pushing the boundaries of fashion with innovative techniques and materials, such as the use of 3D printing in fabric creation (kwertz1120161, 2020; Saunders, 2021).
- The trend towards "quiet luxury," which favours understated elegance and quality, indicates a shift in consumer values towards sustainable and mindful consumption. Brands should emphasise craftsmanship, timeless design, and high-quality materials in their marketing.
- Example: The rise of brands like Loro Piana and The Row, which embody the quiet luxury trend, demonstrates the appeal of this approach (Nichols, 2023).
- Enhance Supply Chain Resilience
- To mitigate risks from geopolitical tensions and other disruptions, luxury brands should diversify their supply chains, invest in local production, and use data analytics for better inventory management.
- Example: Brands that enhance supply chain resilience can better navigate disruptions and maintain consistent product availability (Luxury market outlook: J.P. Morgan Research 2023; Luxury fashion market size, share, industry analysis 2024-32, 2023).
- Leverage Influencer Marketing and High-Profile Collaborations
- Collaborating with influencers and celebrities can significantly boost brand visibility and appeal to younger consumers. Strategic partnerships and user-generated content can drive engagement and increase brand loyalty.
- Example: Louis Vuitton’s successful influencer collaborations and high-profile events have effectively enhanced its market position (Elevating luxury: Exploring marketing strategies of Louis Vuitton, 2023; Louis Vuitton, a Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study, 2023).
- Expand into Emerging Markets
- With strong growth in luxury consumption in markets like China, brands should focus on expanding their presence in these regions. Tailoring products and marketing strategies to local preferences can capture a larger market share.
- Example: The reopening of China's economy presents significant opportunities for luxury brands to tap into the growing demand for luxury goods (Luxury market outlook: J.P. Morgan Research 2023).
Conclusion
By embracing digital innovation, focusing on sustainability, adapting to evolving consumer behaviours, enhancing supply chain resilience, leveraging influencer marketing, and capitalising on emerging markets, luxury fashion brands can navigate the current challenges and secure long-term growth and success in the UK and beyond. These strategies will help maintain their market position and appeal to an increasingly discerning and socially conscious consumer base.
Recommended Academic Papers
1. Experience and Attitude Towards Luxury Brands Consumption in an Emerging Market
(Jhamb et al., 2020)
- Recommendation: This paper is highly recommended for students and marketers interested in understanding consumer behavior in emerging markets. It provides a comprehensive analysis of how sensory, intellectual, behavioral, and affective experiences shape consumer attitudes towards luxury brands.
- Key Points:
- The study highlights the importance of experiential marketing in influencing consumer attitudes and purchase intentions.
- It underscores the role of post-purchase experiences in shaping long-term brand loyalty.
- The research focuses on a young demographic in an emerging market, offering insights into a growing consumer base.
- What Did I Learn?:
- Understanding the various dimensions of consumer experiences can help marketers tailor their strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The paper reveals that positive sensory and emotional experiences significantly boost consumer affinity towards luxury brands.
- What Makes it a Good Academic Paper?:
- The paper is methodologically robust, with a clear research framework and detailed analysis.
- It offers practical implications for luxury brand managers looking to expand their market in emerging economies.
- The study is well-referenced and grounded in existing literature, providing a solid theoretical foundation.
The following graphic from the paper illustrates the relationships between various types of experiences (Sensory, Intellectual, Behavioural, Affective) and different aspects of attitude (Behavioural, Affective, Cognitive) towards luxury brand consumption.
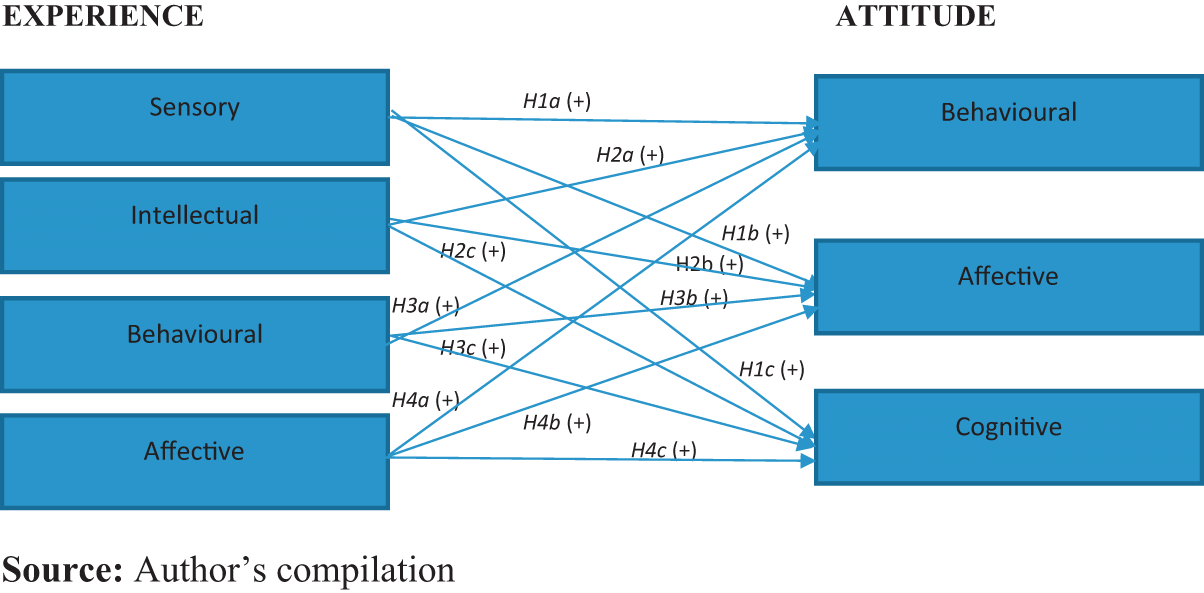
(Jhamb et al., 2020)
As shown in the graphic, the authors hypothesise several positive relationships (denoted by H1a, H2a, etc.) between these variables. For instance, Sensory experience is hypothesised to positively affect Behavioural, Affective, and Cognitive attitudes. The detailed network of these hypotheses provides a comprehensive framework to understand how different experiences shape consumer attitudes towards luxury brands.
This visual representation underscores the complex interplay between experience and attitude, highlighting the importance of considering multiple dimensions when analysing consumer behaviour in the luxury market. Such an approach can offer deeper insights for marketers aiming to enhance brand perception and engagement in emerging markets.
2. Sustainable Luxury Marketing: A Synthesis and Research Agenda
(Athwal et al., 2019)
- Recommendation: This paper is essential reading for those interested in the intersection of sustainability and luxury marketing. It provides a thorough review of the current literature and identifies key themes and future research directions.
- Key Points:
- The paper synthesizes existing research on sustainable luxury, highlighting the growing consumer demand for ethical and environmentally friendly products.
- It identifies key challenges luxury brands face in implementing sustainable practices while maintaining their exclusivity and premium image.
- The study suggests a research agenda to explore unexplored areas in sustainable luxury marketing.
- What Did I Learn?:
- Sustainable practices are not just a trend but a critical component of future luxury brand strategies.
- The paper offers insights into how brands can balance sustainability with luxury to meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
- What Makes it a Good Academic Paper?:
- The paper provides a comprehensive and systematic review of existing literature, making it an excellent starting point for further research.
- It offers clear and actionable recommendations for both researchers and practitioners.
- The paper is well-structured, with a logical flow and clear articulation of key concepts.
The following graphic from the paper presents a timeline of key developments in the realm of sustainable luxury from 2003 to 2017.

(Athwal et al., 2019)
As depicted in the graphic, significant milestones such as the establishment of the Ethical Fashion Forum in 2002, the publication of influential books like "Delux: How luxury lost its luster" in 2007, and the enactment of the Modern Slavery Act in 2015 are highlighted. This timeline effectively encapsulates the growing emphasis on ethical and sustainable practices within the luxury sector over the years.
This visual representation underscores the progressive journey and pivotal moments that have shaped the discourse on sustainable luxury. It is an essential resource for understanding how the industry has evolved and where it is headed. Marketers and researchers can gain valuable insights from this historical context to inform their strategies and further the agenda of sustainability in luxury marketing.
3. Mastering the Digital Transformation as a Heritage Luxury Fashion Brand
(Duma et al., 2020)
- Recommendation: This case study is recommended for those interested in digital transformation within the luxury sector. It provides practical insights into how heritage brands can navigate the digital landscape without compromising their traditional values.
- Key Points:
- The study examines the challenges and opportunities heritage luxury brands face during digital transformation.
- It provides specific strategies and recommendations for integrating digital technologies while preserving brand heritage.
- The paper highlights the importance of balancing innovation with tradition in maintaining brand authenticity.
- What Did I Learn?:
- Digital transformation is crucial for luxury brands to stay competitive, but it must be carefully managed to avoid diluting brand heritage.
- The paper demonstrates that successful digital transformation requires a strategic approach that aligns with the brand's core values and identity.
- What Makes it a Good Academic Paper?:
- The paper uses a detailed case study methodology, providing real-world examples and practical insights.
- It offers a balanced perspective, discussing both the benefits and challenges of digital transformation.
- The study is well-supported by data and references, enhancing its credibility and relevance.
Conclusion
These three papers provide comprehensive insights into key challenges and strategies in the luxury fashion sector. They cover consumer behavior, sustainability, and digital transformation, offering valuable knowledge for students and marketers aiming to understand and navigate the complexities of this industry. Each paper is methodologically sound, well-referenced, and provides actionable recommendations, making them excellent resources for academic and practical applications.
Overall Conclusion
Recap of the Main Points
The UK luxury fashion industry is navigating a complex landscape marked by significant challenges and opportunities. Key marketing issues include economic uncertainty, digital transformation, sustainability demands, evolving consumer behaviour, and supply chain disruptions. Brands like Gucci, Louis Vuitton, and Burberry are leading the way by embracing digital innovation, focusing on sustainability, and adapting to changing consumer preferences.
- Economic Uncertainty: Luxury brands must emphasise the enduring value and investment potential of their products to appeal to more selective consumers amidst economic volatility.
- Digital Transformation: Investing in advanced technologies and maintaining a robust online presence is crucial for engaging with digital-savvy consumers and staying competitive.
- Sustainability Demands: Integrating sustainable practices into core business strategies and being transparent about these efforts are essential for building consumer trust and loyalty.
- Evolving Consumer Behaviour: Understanding and adapting to the preferences of younger generations, who prioritise authenticity and sustainability, is key to maintaining relevance.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Enhancing supply chain resilience through diversification and local production can help mitigate risks and ensure consistent product availability.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Marketing in Luxury Fashion
Marketing plays a pivotal role in the success of luxury fashion brands. It is through innovative and strategic marketing efforts that brands can navigate the complexities of the modern market, maintain their prestigious status, and appeal to an increasingly discerning and socially conscious consumer base. Effective marketing strategies that embrace digital transformation, prioritise sustainability, and adapt to evolving consumer behaviours are essential for luxury brands to thrive in a competitive and rapidly changing environment.
As the industry continues to evolve, the importance of marketing in shaping brand perception, driving consumer engagement, and fostering brand loyalty cannot be overstated. Luxury fashion brands that successfully implement these strategies will not only secure their market position but also set new standards for excellence in the industry. Through a thoughtful and comprehensive approach to marketing, luxury brands can continue to captivate and inspire their audiences, ensuring long-term success and growth.
References:
20 surprising influencer marketing statistics (2024) Digital Marketing Institute. Available at: https://digitalmarketinginstitute.com/blog/20-influencer-marketing-statistics-that-will-surprise-you (Accessed: 25 June 2024).
Alsop, T. (2024) Metaverse market size 2022-2032, Statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1295784/metaverse-market-size/ (Accessed: 25 June 2024).
Athwal, N. et al. (2019) ‘Sustainable Luxury Marketing: A synthesis and research agenda’, International Journal of Management Reviews, 21(4), pp. 405–426. doi:10.1111/ijmr.12195.
Bai, H., McColl, J. and Moore, C. (2021) ‘Luxury fashion retailers’ localised marketing strategies in practice – evidence from China’, International Marketing Review, 39(2), pp. 352–370. doi:10.1108/imr-02-2021-0079.
Boyd, D. (2023) Council post: Luxury fashion meets immersive commerce: Luxury in the Metaverse Era, Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2023/02/09/luxury-fashion-meets-immersive-commerce-luxury-in-the-metaverse-era/#:~:text=In%202022%2C%20brands%20like%20Louis,early%20adopters%20of%20the%20metaverse. (Accessed: 25 June 2024).
Brito, M., Carbone, V., & Blanquart, C., 2008. Towards a sustainable fashion retail supply chain in Europe: Organisation and performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 114, pp. 534-553. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPE.2007.06.012.
Brun, A., Caniato, F., Caridi, M., Castelli, C., Miragliotta, G., Ronchi, S., Sianesi, A., & Spina, G., 2008. Logistics and supply chain management in luxury fashion retail: Empirical investigation of Italian firms. International Journal of Production Economics, 114, pp. 554-570. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPE.2008.02.003.
Cassidy, T., 2017. Conceptualizing Sustained High Quality Fashion Products in a Devalue Dominated Marketplace. Fashion Practice, 9, pp. 235 - 253. https://doi.org/10.1080/17569370.2016.1220136.
Choi, T., & Liu, N., 2019. Optimal advertisement budget allocation and coordination in luxury fashion supply chains with multiple brand-tier products. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2019.08.009.
Duma, F. et al. (2020) ‘Mastering the Digital Transformation as a heritage luxury fashion brand’, Marché et organisations, n° 37(1), pp. 33–54. doi:10.3917/maorg.037.0033.
Elevating luxury: Exploring marketing strategies of Louis Vuitton (2023) The Brand Hopper. Available at: https://thebrandhopper.com/2023/07/18/elevating-luxury-exploring-marketing-strategies-of-louis-vuitton/ (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Franco, J., Hussain, D., & McColl, R., 2019. Luxury fashion and sustainability: looking good together. Journal of Business Strategy. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBS-05-2019-0089.
Grassi, A. (2020) ‘Art to enhance consumer engagement in the luxury fashion domain’, Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal, 24(3), pp. 327–341. doi:10.1108/jfmm-09-2019-0194.
Gucci Digital Marketing, Advertising & Strategy Case Study: G & Co.. (2024) Gucci Digital Marketing, Advertising & Strategy Case Study | G & Co. Available at: https://www.g-co.agency/insights/gucci-advertising-strategy-case-study (Accessed: 27 June 2024).
Hall, H. (2020) Burberry takes to twitch to livestream collection that sees Riccardo Tisci hit his stride, The Independent. Available at: https://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/fashion/burberry-ss21-review-london-fashion-week-bella-hadid-twitch-stream-b466393.html (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Han, J., Seo, Y., & Ko, E., 2017. Staging luxury experiences for understanding sustainable fashion consumption: A balance theory application. Journal of Business Research, 74, pp. 162-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JBUSRES.2016.10.029.
He, H., Jiang, Y., & Wang, Y., 2022. Research on Marketing Strategy for the Male Market Luxury Industry — Taking Dior as an Example. Journal of Economics, Business and Management. https://doi.org/10.18178/joebm.2022.10.3.694.
Henninger, C., Alevizou, P., Tan, J., Huang, Q., & Ryding, D., 2017. Consumption strategies and motivations of Chinese consumers: The case of UK sustainable luxury fashion. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, 21, pp. 419-434. https://doi.org/10.1108/JFMM-05-2017-0046.
Hilken, T., Chylinski, M., Keeling, D., Heller, J., Ruyter, K., & Mahr, D. (2021). How to strategically choose or combine augmented and virtual reality for improved online experiential retailing. Psychology & Marketing. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21600.
Immersive tech week 2022 | Virtual Fashion & Virtual Bodies (2023) YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HMtu5jm5sHY (Accessed: 25 June 2024).
Jhamb, D. et al. (2020) ‘Experience and attitude towards luxury brands consumption in an emerging market’, European Business Review, 32(5), pp. 909–936. doi:10.1108/ebr-09-2019-0218.
Jung, S., & Jin, B., 2016. From quantity to quality: understanding slow fashion consumers for sustainability and consumer education. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 40, pp. 410-421. https://doi.org/10.1111/IJCS.12276.
Karaosman, H., Perry, P., Brun, A., & Morales-Alonso, G., 2020. Behind the runway: Extending sustainability in luxury fashion supply chains. Journal of Business Research, 117, pp. 652-663. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JBUSRES.2018.09.017.
Kim, A., & Ko, E., 2010. Impacts of Luxury Fashion Brand’s Social Media Marketing on Customer Relationship and Purchase Intention. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing, 1, pp. 164 - 171. https://doi.org/10.1080/20932685.2010.10593068.
Kim, J., & Lee, H., 2011. The Impact of Shopping Orientations on U.S. Consumer’s Retail Channel Choice Behavior toward Luxury Goods Purchases*. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing, 2, pp. 188 - 199. https://doi.org/10.1080/20932685.2011.10593097.
Kim, S., & Ma, J., 2019. A study on the digital transformation strategy of a fashion brand. The Research Journal of the Costume Culture. https://doi.org/10.29049/rjcc.2019.27.5.449.
Kohrs, K., 2020. The language of luxury fashion advertising: technology of the self and spectacle. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/jfmm-02-2020-0029.
kwertz1120161 (2020) McQueen reigns the Fashion Tech Revolution, SIRIUS. Available at: https://www.sirius.london/post/mcqueen-reigns-the-fashion-tech-revolution (Accessed: 01 July 2024).
Liu, Y., 2023. Analysis on Chanel Group Digital Marketing Strategies. Journal of Education, Humanities and Social Sciences. https://doi.org/10.54097/ehss.v16i.9598.
Louis Vuitton, a Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study (2023) G & Co. Available at: https://www.g-co.agency/insights/louis-vuitton-advertising-strategy-case-study (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Luxury fashion market size, share, industry analysis 2024-32 (2023) Size, Share, Industry Analysis 2024-32. Available at: https://www.imarcgroup.com/luxury-fashion-market (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Luxury market outlook: J.P. Morgan Research (2023) Luxury market outlook | J.P. Morgan Research. Available at: https://www.jpmorgan.com/insights/global-research/retail/luxury-market (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Ma, Y., 2022. The Research on the Marketing Strategies of Luxury Brands and its Extension—Taking Tiffany & Co. as an Example. BCP Business & Management. https://doi.org/10.54691/bcpbm.v33i.2710.
Macchion, L., Danese, P., & Vinelli, A., 2015. Redefining supply network strategies to face changing environments. A study from the fashion and luxury industry. Operations Management Research, 8, pp. 15-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12063-014-0097-6.
Mastering luxury: Burberry Marketing Strategies & Marketing Mix (2023) The Brand Hopper. Available at: https://thebrandhopper.com/2023/07/25/mastering-luxury-burberry-marketing-strategies-marketing-mix/#google_vignette (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Matić, L. and Pandža Bajs, I. (2022a) ‘Specificity and development of distribution strategies of luxury fashion brands’, Textile & Leather Review, 5, pp. 540–563. doi:10.31881/tlr.2022.69.
Nichols, K. (2023) The 2023 luxury report: The brands, items, and trends defining designer fashion, WhoWhatWear. Available at: https://www.whowhatwear.com/luxury-report-2023 (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
O’, Y. (2024) Burberry’s Digital Transformation and Brand Revival — How Burberry used digital media to rejuvenate its classic image, Medium. Available at: https://medium.com/@SavvyYeni/burberrys-digital-transformation-and-brand-revival-how-burberry-used-digital-media-to-rejuvenate-c2e16c5aa944#:~:text=By%20implementing%20a%20range%20of,that%20resonated%20with%20its%20audience.&text=Burberry%20recognized%20the%20power%20of,engaging%20with%20a%20global%20audience. (Accessed: 24 June 2024).
Olatubosun, P., Charles, E., & Omoyele, T., 2021. Rethinking luxury brands and sustainable fashion business models in a risk society. Journal of Design, Business & Society. https://doi.org/10.1386/DBS_00020_1.
Peng, F., An, N., & Vecchi, A., 2017. Cross-Cultural Study of Online User Behavior in Fashion E-Commerce: A Comparison of Britain and China. , pp. 277-293. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-1865-5.CH012.
Polat, V., 2021. Digital Transformation of Luxury Brands. Advances in Marketing, Customer Relationship Management, and E-Services. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-7192-7.ch005.
Rahman, A., 2023. Online Luxury Consumer’s Brands Loyalty among Bangladeshi Women in East London. Transnational Business and Management. https://doi.org/10.33182/tbm.v1i2.3198.
Riar, M., Xi, N., Korbel, J., Zarnekow, R., & Hamari, J. (2022). Using augmented reality for shopping: a framework for AR induced consumer behavior, literature review and future agenda. Internet Res., 33, 242-279. https://doi.org/10.1108/intr-08-2021-0611.
Romo, Z., Medina, I., & Romero, N., 2017. Storytelling and Social Networking as Tools for Digital and Mobile Marketing of Luxury Fashion Brands. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol., 11, pp. 136-149. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v11i6.7511.
Rosenbaum, G., Carneiro, M., Gomes, C., & Marques, L., 2022. Designing a Digital Marketing Strategy for Start-Up Luxury Brands. Handbook of Research on Smart Management for Digital Transformation. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-9008-9.ch021.
Saunders, S. (2021) 3D printing hits the runway with a unique Alexander McQueen/VOJD Studios umbrella - 3dprint.com: The Voice of 3D printing / additive manufacturing, 3DPrint.com | The Voice of 3D Printing / Additive Manufacturing. Available at: https://3dprint.com/155800/high-fashion-3d-printed-umbrella/ (Accessed: 24th June 2024).
Savelli, E., 2011. Role of Brand Management of the Luxury Fashion Brand in the Global Economic Crisis: A Case Study of Aeffe Group. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing, 2, pp. 170 - 179. https://doi.org/10.1080/20932685.2011.10593095.
Statista. (2024). Luxury Fashion - United Kingdom. [online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/luxury-goods/luxury-fashion/united-kingdom [Accessed 1 July 2024].
Tsai, S., 2005. Impact of Personal Orientation on Luxury-Brand Purchase Value: An International Investigation. International Journal of Market Research, 47, pp. 427 - 452. https://doi.org/10.1177/147078530504700403.
Wang, Y., 2021. How Fashion Luxury Brands Innovate Marketing Strategies in the Development of Internet Media. BCP Business & Management. https://doi.org/10.54691/bcpbm.v16i.304.
Wood, S., Watson, I. and Teller, C. (2021) ‘Pricing in online fashion retailing: Implications for research and Practice’, Journal of Marketing Management, 37(11–12), pp. 1219–1242. doi:10.1080/0267257x.2021.1900334.
Wrigley, C. and Straker, K., 2019. Affected: Emotionally engaging customers in the digital age. John Wiley & Sons.
Zhang, X., 2023. The Influence of Mass Media on Luxury Fashion Brand Marketing Strategies: A Case Study of Herms. Communications in Humanities Research. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7064/21/20231410.
Zhu, Z., 2023. The Impact of Digital Transformation on the Fashion Industry in the Post-Pandemic Era. BCP Business & Management. https://doi.org/10.54691/bcpbm.v44i.4920.